Pistachio is one of Armenia's most important horticultural crops. Stomatal density, a critical characteristic of pistachio leaves, can significantly affect gas exchange processes in plants.
Effective water and soil management can influence stomatal density, ultimately affecting plant health and productivity.
Water testing for irrigation purposes generally falls into three categories: bacteriological, mineral/inorganic, and organic chemical tests. Mineral tests often check for elements like calcium, magnesium, manganese, iron, copper, and zinc.
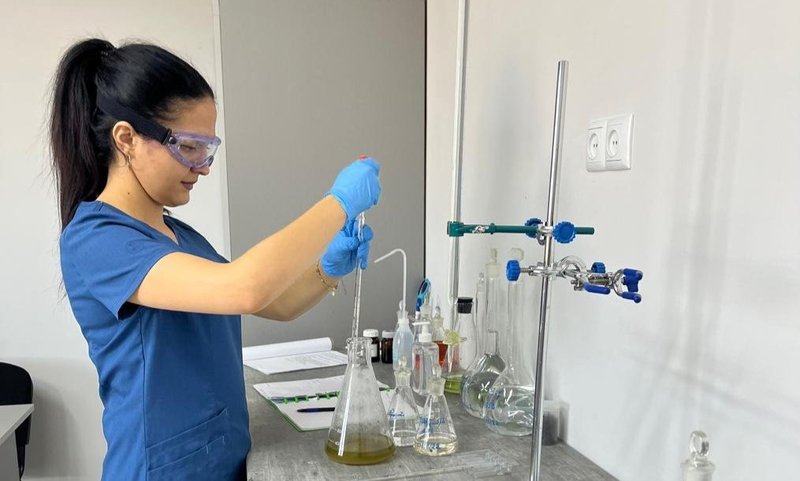
Organic matter plays an essential role in crop production and soil health by improving the physical, chemical, and biological properties of the soil.
In the image below you can see the process of determination of soil organic matter by using the titrimetric method.

Soils can be naturally acid or alkaline, and this can be measured by testing their pH value. Soil pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the soil.
Soil electrical conductivity (EC) measures the salt content in soil and serves as an indicator of soil health. Soil EC is an index that provides insight into the level of water-soluble salts, which are vital for assessing mineral nutrients in topsoil that plants can quickly absorb. This is also a key factor in determining whether salt ions in the soil may limit crop growth.
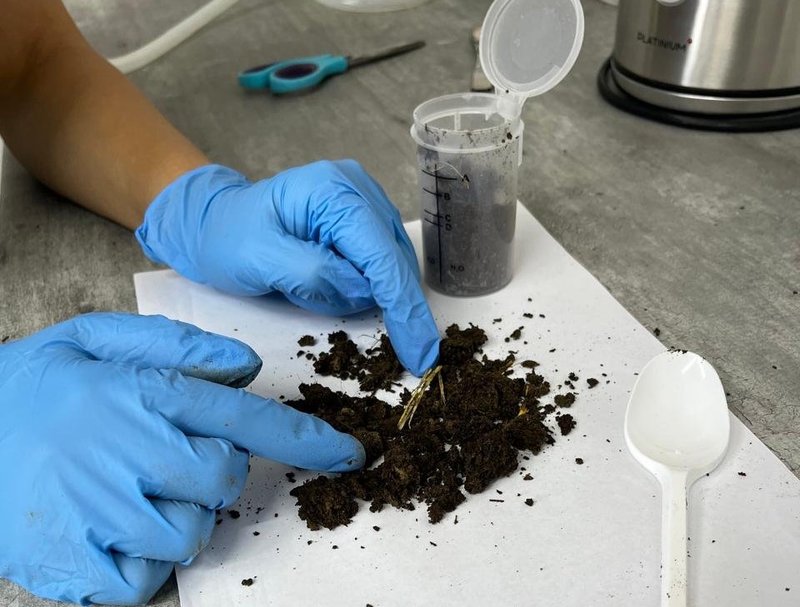

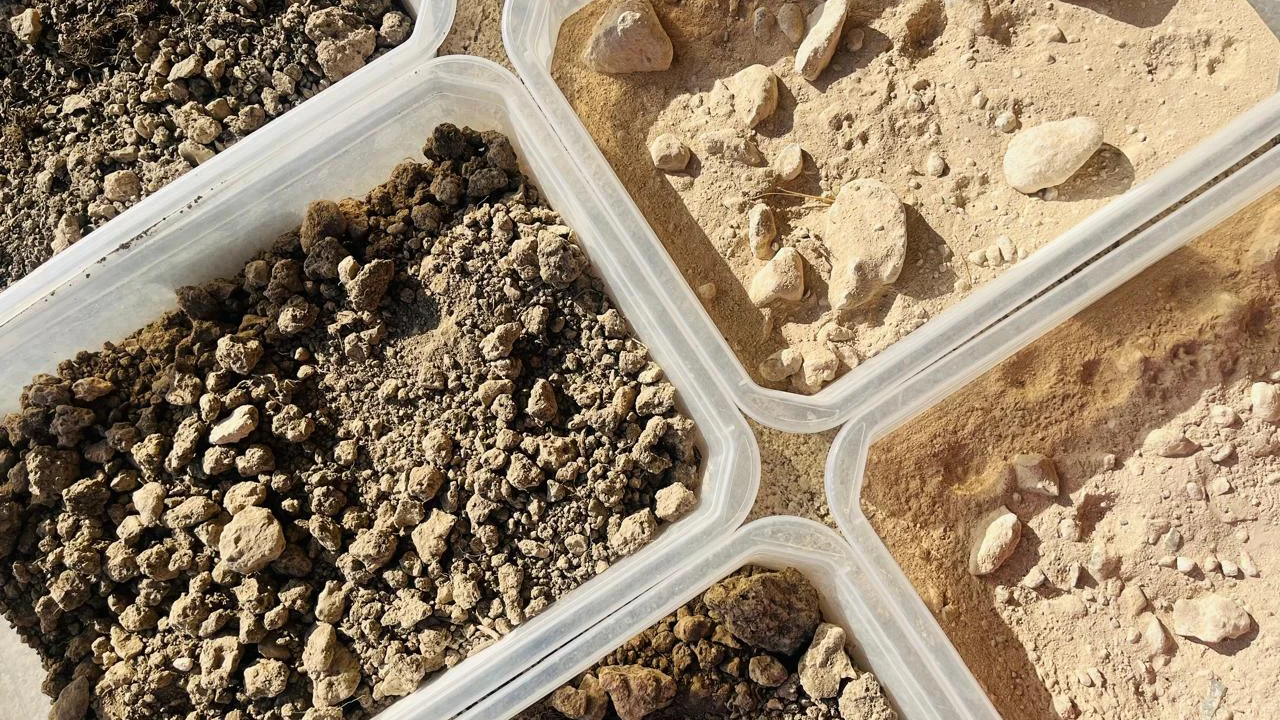
Soil sampling is the process of taking a small sample of soil, which is then sent to a lab to determine the nutrient content. The soil can also be tested for the chemical, physical and biological properties, which are critical to plant nutrition.
When done right, soil sampling can provide a representative snapshot of fertility across an agricultural field–providing growers with critical information to make their best management decisions.
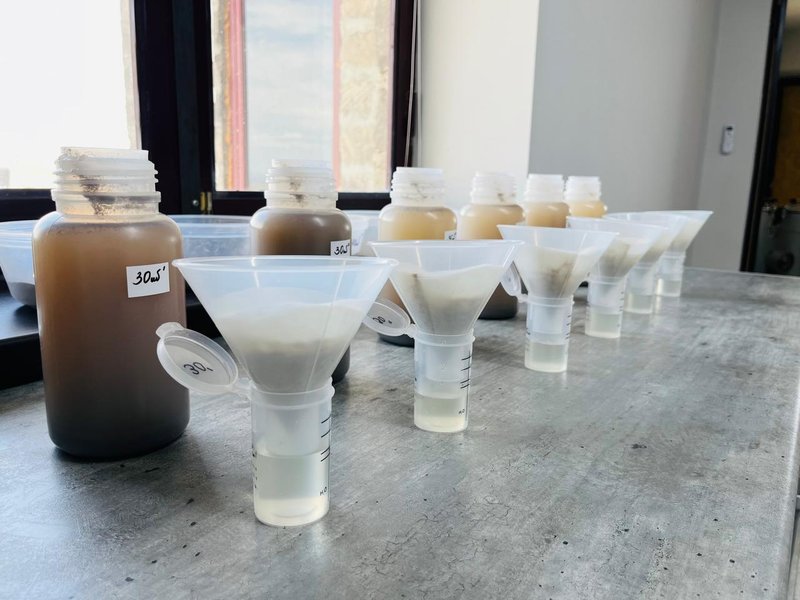
Finally, soil extract filtration involves preparing a clear solution for further analysis.